Ozone (O3) is a gas. High in the atmosphere, it protects us from UV radiation. But at ground level, ozone is a pollutant.
Ozone can occasionally cause poor air quality during summer. It’s the main pollutant in summer smog. We measure ozone at some of our air monitoring sites.
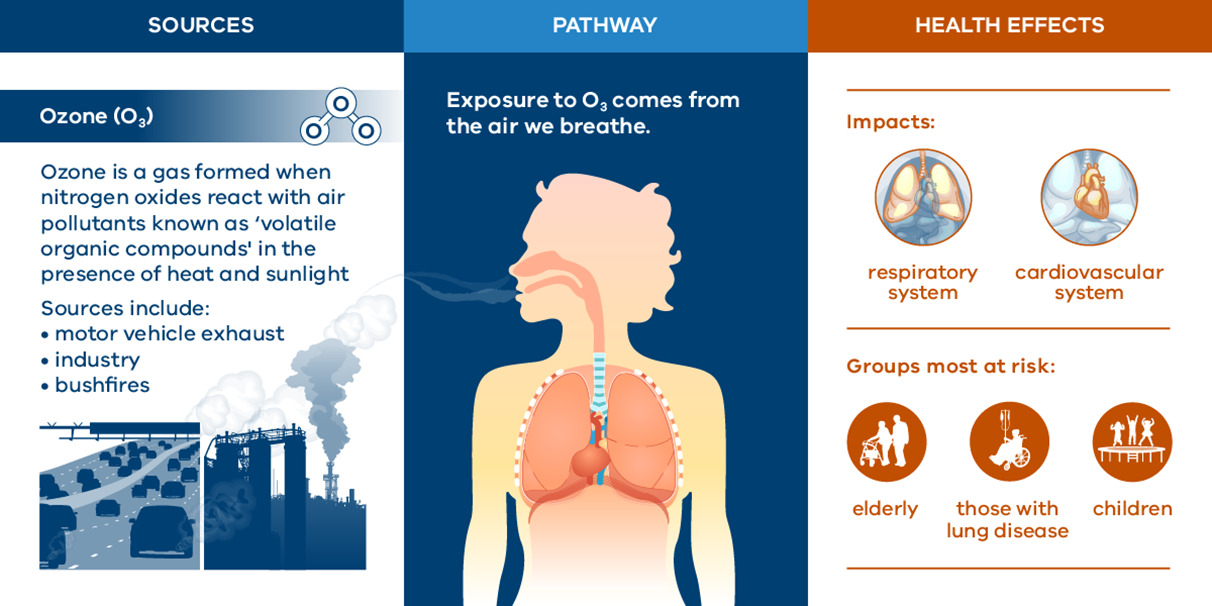
Sources of ozone
Ozone forms when volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and nitrous oxides react together in the atmosphere. This happens during warm, sunny weather. The main sources of VOCs and nitrous oxides include:
- car and truck exhausts
- bushfire smoke
- power stations
- industry.
Read more about ozone depleting substances.
Read more about protecting the ozone layer.
Health effects of ozone
Breathing in high levels of ozone can irritate the lining of your throat and lungs. This can make it difficult to breathe. People most sensitive to ozone include:
- those with lung conditions
- children
- people over 65.
Ozone on EPA AirWatch
We show ozone data on EPA AirWatch using air quality categories.
| Air quality category | Ozone averaged over 1 hour (parts per billion) |
|---|---|
| Good | Less than 50 |
| Moderate | 50–100 |
| Poor | 100–150 |
| Very poor | 150–300 |
| Hazardous | More than 300 |
Current standards for ozone
| National standard, in parts per million (and parts per billion) | Averaging time |
|---|---|
| 0.065 ppm (65 ppb) | 8 hours |
| Environment Reference Standard | |
| 0.060 ppm (60 ppb) | 8 hours |
Read more about air quality
Vehicle emissions and air quality
Reviewed 30 March 2022



